42 kinetic energy word problems
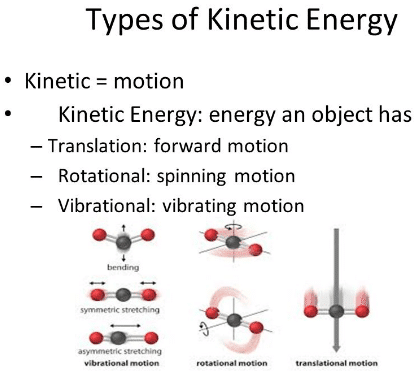
PDF Kinetic Energy Practice Problems Kinetic Energy Practice Problems 1. What is the Kinetic Energy of a 150 kg object that is moving with a speed of 15 m/s? 2. An object has a kinetic energy of 25 J and a mass of 34 kg , how fast is the object moving? 3. An object moving with a speed of 35 m/s and has a kinetic energy of 1500 J, what is the mass of the object. 4. Kinetic energy | Definition, Formula, Units, Examples, & Facts Kinetic energy is a property of a moving object or particle and depends not only on its motion but also on its mass. The kind of motion may be translation (or motion along a path from one place to another), rotation about an axis, vibration, or any combination of motions.
Kinetic Energy Problems and Solutions - Basic-mathematics.com Kinetic energy problems When solving kinetic energy problems, you may be asked to find 3 variables. These variables are the kinetic energy, the mass, or the speed. Problem # 1: Suppose a car has 3000 Joules of kinetic energy. What will be its kinetic energy if the speed is doubled? What if the speed is tripled? Solution:

Kinetic energy word problems
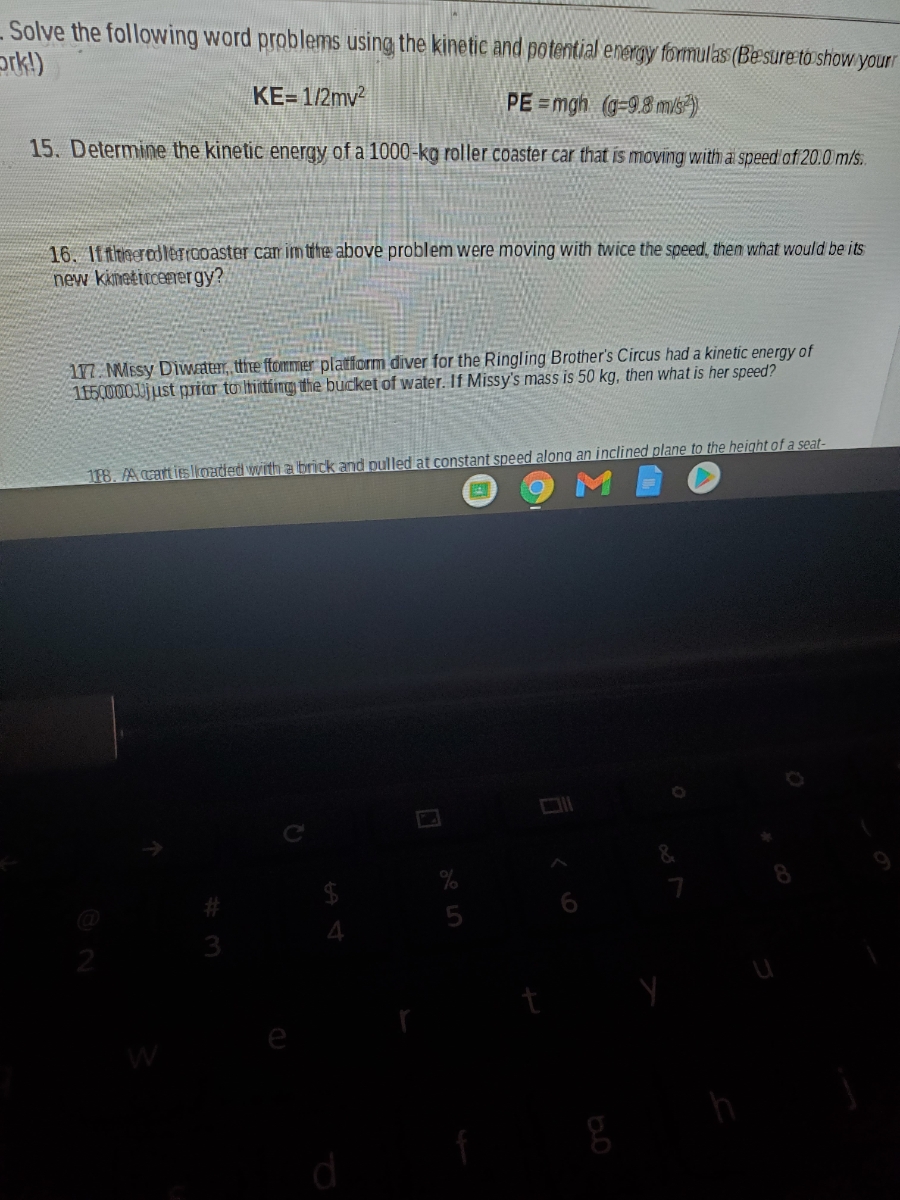
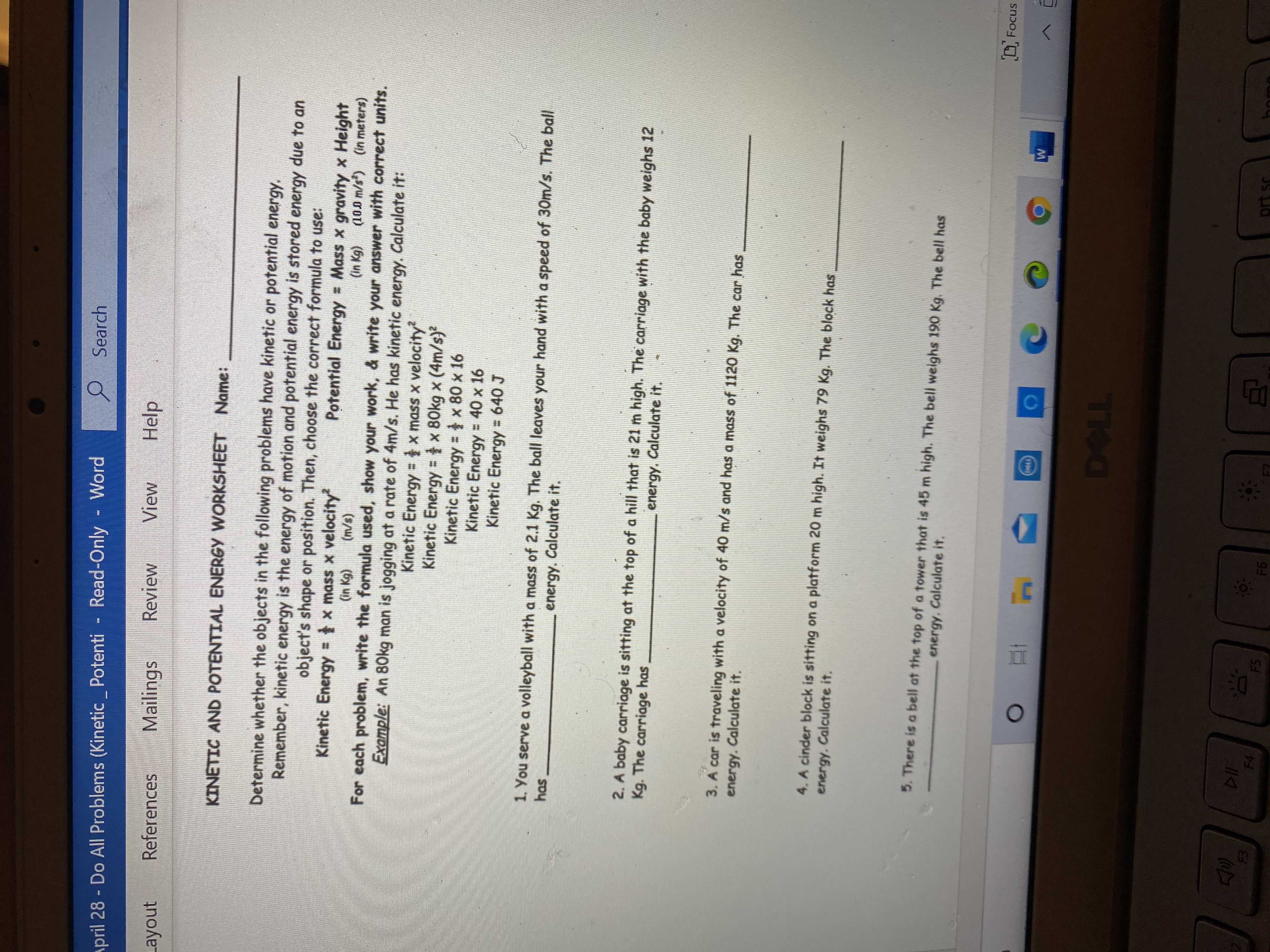
DOC Energy Problems (Kinetic and GPE) - Henry County Schools Energy Problems (Kinetic and GPE) Key. Work the following problems on a separate sheet of paper - use the 4 steps for solving physics problems. KE = ½ m x v2 GPE = m x g x h. A cheetah can run briefly with a speed of 31 m/s. Suppose a cheetah with a mass of 47 kg runs at this speed. What is the cheetah's kinetic energy? PDF Worksheet: Kinetic and Potential Energy Problems 17. Calculate the kinetic energy of the rock in problem #8 if the rock rolls down the hill with a velocity of 8 m/s. 18. Calculate the kinetic energy of a truck that has a mass of 2900 kg and is moving at 55 m/s. 19. Find the mass of a car that is traveling at a velocity of 60 m/s North. The car has 5,040,000 J of kinetic energy. 20. Edkinderson Maxi - PE and KE word problems 1 .pdf - Course Hero KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY WORKSHEET Name:_____ Determine whether the objects in the following problems have kinetic or potential energy. Then choose the correct formula to use: KE = 1/2 m v 2 OR PE = mgh = F w 1. You serve a volleyball with a mass of 2.1 kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 30 m/s.
Kinetic energy word problems. What is kinetic energy? (article) | Khan Academy Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion. If we want to accelerate an object, then we must apply a force. Applying a force requires us to do work. After work has been done, energy has been transferred to the object, and the object will be moving with a new constant speed. Kinetic and Potential Energy word problems Flashcards | Quizlet solving for kinetic energy, the formula is... KE = 0.5 • m • v2 what does m stand for? mass of the object was does v stand for? speed of the object to solve for mass (KE) , the formula would be... m= (2xKE) ÷ v2 to solve for velocity (KE), the formula would be... √ (2⋅KE) ÷ m to find gravitational potential energy, the formula would be... m⋅g⋅h Kinetic Energy Formula | Problems (With Solutions) - Learnool Kinetic Energy Practice Problems Problem 1: A ball of mass 3 kg is moving with the velocity of 6 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of a ball. Solution: Given data: Mass of a ball, m = 3 kg Velocity of a ball, v = 6 m/s Kinetic energy of a ball, KE = ? Using the formula of kinetic energy, KE = ½ × m v 2 KE = ½ × 3 × (6) 2 KE = ½ × 3 × 36 KE = 54 J Kinetic energy problems and solutions - api.3m.com The kinetic energy of an object can be calculated using the formula: KE = 0.5 * m * v^2. Where KE is the kinetic energy, m is the mass of the object, and v is the velocity of the object. One common problem with kinetic energy is that it can be difficult to measure. This is because kinetic energy is a type of potential energy, which means that ...
DOCX Mr. Blaikie's site - Home Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet. Classify the following as a type of potential energy or kinetic energy (use the letters K or P) 1. A bicyclist pedaling up a hill __K___ ... Solve the following word problems using the kinetic and potential energy formulas (Be sure to show your work!) Formulas: KE = 0.5 x m x v. 2. OR. PE = m x g x h. Practice Problems on Potential Energy - GeeksforGeeks Let's see some problems based on these concepts. Sample Problems Question 1: A mass of 2Kg is taken from the ground to the height of 10m. Find the potential energy of the object. Answer: The potential energy of a mass 'm' at the height 'h' is given by, P = mgh Given: m = 2kg and g = 10 m/s 2 and h = 10m. Aim: Find the potential energy. Word problems kinetic and potential energy - Quizizz What is the cheetah's kinetic energy? answer choices 1457 Joules 22,584 Joules 15 Joules 45,167Joules Question 8 180 seconds Q. Calculate the kinetic energy of a moving 4 kg object travelling at a velocity of 3 m/s. answer choices 18 J 36 J 12 J 6 J Question 9 180 seconds Q. Kinetic Energy Word Problems | Online Science Help Introduction to kinetic energy word problems: Energy is a capacity to do work. The energy gained or lost due to motion, position or configuration is called mechanical energy. It is of two types. Kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy = 1/2 Mv 2 Where M is mass of the body and v = velocity
Potential And Kinetic Energy Example Problem - Work and Energy Examples Kinetic energy is the energy of the object in motion. It is expressed by the formula KE = ½mv 2 where KE is the kinetic energy m is the mass of the object v is the velocity of the object. The total energy of the system is conserved at any point of the system. The total energy is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy. Kinetic Energy Worksheet Teaching Resources | TPT - TeachersPayTeachers A 2-page worksheet product designed to help upper middle school and lower high school students review to the topic of solving gravitational potential energy (GPE=mgh) and kinetic energy (KE=1/2MV2) calculations through a set of 10 word problems.Product Contents:Pages 1-2 - GPE and KE Word Problems:Formulas for GPE and KE4 leveled word problems … Work, Energy, and Power Problem Sets - Physics Classroom What is Jerome's kinetic energy at the end of this acceleration period? c. Once the launch is over, Jerome begins screaming up the 420-foot, completely vertical section of the track. Determine Jerome's potential energy at the top of the vertical section. (GIVEN: 1.00 m = 3.28 ft) d. Determine Jerome's kinetic energy at the top of the vertical ... PDF Kinetic Energy Practice Problems - MS BOURBONNAIS TEACHING Kinetic Energy Practice Problems 1. What is the Kinetic Energy of a 150 kg object that is moving with a speed of 15 m/s? KE = ½ mv2 KE = ? m = 150kg v = 15m/s KE = ½ (150kg) (15 m/s)2 KE = ½ (150kg)(225) KE = 16875J 2. An object has a kinetic energy of 25 J and a mass of 34 kg , how fast is the object moving? KE = ½ mv2
Work and kinetic energy - problems and solutions - Basic Physics Work-Kinetic energy: 1. A 5000-kg car accelerated from rest to 20 m/s. Determine the net workdone on the car. Known : Mass(m) = 5000 kg Initial speed (vo) = 0 m/s (car rest) Final speed (vt) = 20 m/s Wanted: net work Solution : The work-kinetic energy principle: Wnet= ΔEK Wnet= ½ m (vt2- vo2) Wnet= net work ΔEK = the change in kinetik energy
Results for kinetic and potential energy word problems Kinetic and Potential Energy Word Problems by Luis Barrera 5.0 (6) $1.50 Word Document File This worksheets include word problems to practice Kinetic and Potential energy formulas. The first worksheet includes KE formula and re-arrangement of the formula to find mass and velocity for each problem.

solve the following word problem using kinetic and potential energy formula be sure to show your work
Mechanical Energy Problem Solutions - StickMan Physics I cancelled out the initial kinetic energy because: KE i = ½ mv f2. KE i = (½) (3.5) (0 2) = 0 J. I cancelled out the final potential energy because: PE f = mgh f. PE f = (3.5) (9.8) (0) = 0 J. (Note: In many of these problems I could cancel out mass but did not since it was provided) Since I did not cancel out mass I could answer the ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy Problem Set - The Biology Corner 1. Find the gravitational potential energy of a light that has a mass of 13.0 kg and is 4.8 m above the ground. m = g = Answer: h = GPE = 2. An apple in a tree has a gravitational potential energy of 175 J and a mass of 0.36 g. How high from the ground is the apple? m = g = Answer: h = GPE = 3. A marble is on a table 2.4 m above the ground.
Kinetic Energy Examples - Online Math Learning Kinetic energy is the energy stored in moving objects. Stationary objects have no kinetic energy. E k = 0.5 × m × v 2 Examples: A car with a mass of 700 kg is moving with a speed of 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the car. A cyclist and bike have a total mass of 100 kg and a speed of 15 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy.
How to Calculate Kinetic Energy: 9 Steps (with Pictures) - WikiHow In some problems, you may know the kinetic energy and the mass or kinetic energy and velocity. The first step to solving this problem is to plug in all of the variables that are known. Example 1: What is the velocity of an object with a mass of 30 kg and a kinetic energy of 500 J? KE = 0.5 x mv2 500 J = 0.5 x 30 x v2
Kinetic Energy Problems Worksheet - onlinemath4all KINETIC ENERGY PROBLEMS WORKSHEET Problem 1 : What is the Kinetic Energy of a 150 kg object that is moving with a speed of 15 m/s? Problem 2 : An object has a kinetic energy of 425 joules and a mass of 34 kg. How fast is the object moving? Problem 3 : An object moving with a speed of 25 m/s and has a kinetic energy of 1875 joules.
Kinetic Energy Word Problems (set 2 Challenge!) Flashcards bottom of the hill, your kinetic energy will be equal to your potential energy at the top. Calculate your speed at the bottom of the hill. (Note: KE=PE) A. Mass x acceleration of gravity= wt in Newtons (60kg) (9.8) = 588N B. 1000J = 588N (h) 588 588 1.7 meters = h C. KE = 1/2mv2 1000J = ½ (60kg) v2 1000 = 30v2 30 30 √33.33= √v 2 5.8 m/s = v
PDF Kinetic and Potential Energy Practice Problems 6. If the bullet in problem #6 is traveling 2 meters of the ground, what would the potential energy of the bullet be? 7. Former Minnesota Vikings Quarterback Brett Favre throws a football at a speed of 35 meters per second. If the weight of the football is 0.4 kg, what would the kinetic energy of Brett Favre's pass be? 8. Mr.
Practice Problems on Kinetic Energy - GeeksforGeeks Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity, and it is expressed in Joules. Sample Problems Question 1: A ball has a mass of 2Kg, suppose it travels at 10m/s. Find the kinetic energy possessed by it. Answer: Given: m = 2Kg, and v = 10m/s The KE is given by, K.E = K.E = ⇒ K.E = ⇒ K.E = 100J
Edkinderson Maxi - PE and KE word problems 1 .pdf - Course Hero KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY WORKSHEET Name:_____ Determine whether the objects in the following problems have kinetic or potential energy. Then choose the correct formula to use: KE = 1/2 m v 2 OR PE = mgh = F w 1. You serve a volleyball with a mass of 2.1 kg. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 30 m/s.
PDF Worksheet: Kinetic and Potential Energy Problems 17. Calculate the kinetic energy of the rock in problem #8 if the rock rolls down the hill with a velocity of 8 m/s. 18. Calculate the kinetic energy of a truck that has a mass of 2900 kg and is moving at 55 m/s. 19. Find the mass of a car that is traveling at a velocity of 60 m/s North. The car has 5,040,000 J of kinetic energy. 20.
DOC Energy Problems (Kinetic and GPE) - Henry County Schools Energy Problems (Kinetic and GPE) Key. Work the following problems on a separate sheet of paper - use the 4 steps for solving physics problems. KE = ½ m x v2 GPE = m x g x h. A cheetah can run briefly with a speed of 31 m/s. Suppose a cheetah with a mass of 47 kg runs at this speed. What is the cheetah's kinetic energy?



























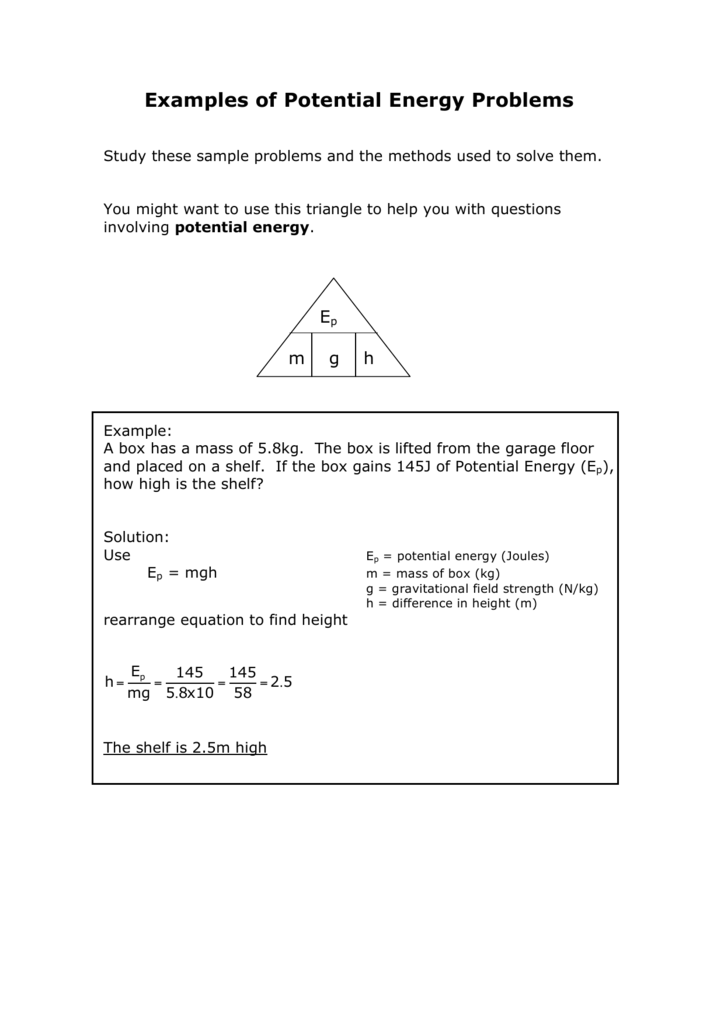



0 Response to "42 kinetic energy word problems"
Post a Comment